 Curious about leveraging technological advances in applied tissue regeneration to improve patient outcomes? Extracorporeal Pulse Activation Technology (EPAT®), also known as ESWT or shockwave, is an evidence-based treatment option that helps restore the body’s natural healing and regenerative processes so patients can feel better faster, without surgery.
Curious about leveraging technological advances in applied tissue regeneration to improve patient outcomes? Extracorporeal Pulse Activation Technology (EPAT®), also known as ESWT or shockwave, is an evidence-based treatment option that helps restore the body’s natural healing and regenerative processes so patients can feel better faster, without surgery.
Since 1980 when acoustic waves were first used to disintegrate kidney stones, the medical potential of regenerative treatment options have been continuously developing across a wide range of fields. Today, EPAT/ESWT is being used to successfully treat numerous musculoskeletal, aesthetic and wound issues and disorders.
What Is Applied Tissue Regeneration?
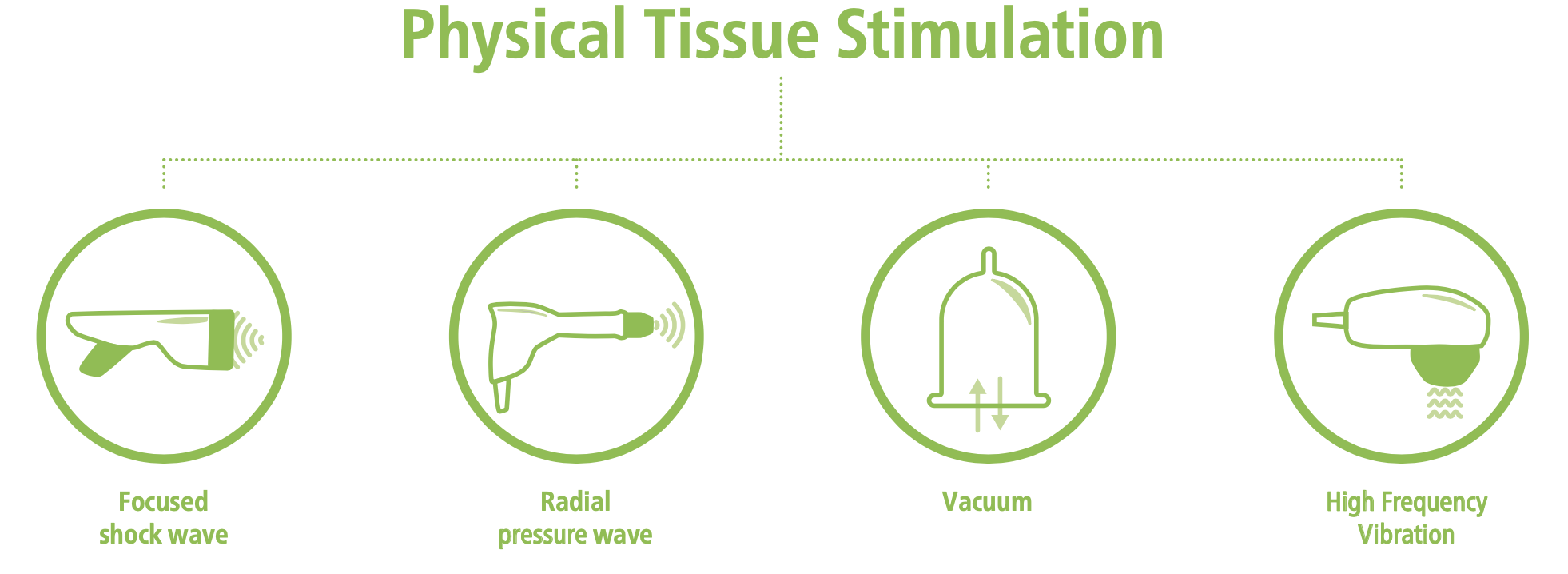
EPAT is based on the science of Applied Tissue Regeneration (ATR), and describes a treatment approach that can complement medication-based protocol. Based on each patient’s specific need, there are a wide range of different physical treatment options, including:
- Focused Shockwave
- Radial Pressure Wave
- High Frequency Vibration (with specialized handpieces)
- Vacuum technology treatments (with products like VACU-ACTOR®)
What Conditions Can Be Treated with Tissue Regeneration Technologies?
A careful combination of evidence-based treatment methods leads to desired outcomes, especially for tendinopathy and myofascial pain syndromes.
The Radial Pressure Wave systems are especially suitable for the following indications:
- Lower extremity pain associated with achillodynia
- Heel pain associated with plantar fasciitis
- Anterior shin pain associated with tibial stress syndrome
- Hip pain associated with trochanteric tendinopathy
- Shoulder pain associated with shoulder tendonitis with or without calcification
- Elbow pain associated with lateral/medial epicondylitis
Examples of indications and regions for trigger point treatment/ acupuncture points include:
- Calf muscles
- Thigh muscles
- Lumbago
- Dorsalgia
- Cervical syndrome
- Cervical spine muscles (atlas)
How to Locate a Patient’s Treatment Area
For your patients, pain points are typically located in two ways: by accurate history-taking and palpation, and by localizing these points by means of EPAT treatment and patient feedback.
Many medical professionals prefer to precisely localize the area for treatment by ultrasound, X-ray or other imaging technique. With ultrasound, you can get an accurate diagnosis to ensure that the indication is definitely one recommended for EPAT. Ultrasound is also useful post treatment to evaluate the treatment outcome.
How to Conduct EPAT Treatment
To help ensure successful treatment, inform your patients about what to expect from treatment. Position patients comfortably, ensuring you have easy access to the area requiring treatment. Most treatments are more effective when used with ultrasound gel, which provides optimum coupling (with the exception of certain cases).
How to Find the Right Intensity Level
The aim during treatment is to adjust the intensity level to the pain level expressed by your patient. Start at a low intensity level and increase this gradually. You’ll find that you can usually increase this at each successive session.
Because the treatment is experienced differently by each patient, it’s important that the intensity of treatment does not exceed the patient’s comfort limits. Otherwise, the muscles may tense up as a protective response.

As with any other new modality, the treatment success will increase as the medical professional gains experience with the operation and use of the EPAT devices. Keep in mind, when you partner with CuraMedix, you have access to responsive support and training and superior customer service at all times.
Interested in more how-to information about EPAT treatment? Request our comprehensive guide for a clear and easy overview on how to operate the technology for optimal results. This reference guide features plenty of sample indications, recommended treatment steps, protocols, useful images and more. To inquire, contact us at any time.


